A CDMO company (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization) delivers end-to-end support across development, scale-up, and commercial manufacturing, enabling organizations to convert complex chemistry into compliant, scalable products. Unlike fragmented outsourcing, CDMOs reduce technical risk, improve manufacturability, and accelerate commercialization.
In this blog, you’ll understand what a CDMO is, how CDMO services work in real-world chemical manufacturing, and what to look for when selecting a CDMO partner—with examples relevant to custom chemicals, intermediates, agrochemicals, and performance materials.
Introduction
Global enterprises across specialty chemicals, agrochemicals, and performance materials face growing pressure to innovate faster while maintaining regulatory compliance, cost control, and supply continuity.
Building all capabilities in-house such as R&D, process engineering, scale-up, EHS, and manufacturing demands heavy capital investment and long lead times.
This is where a CDMO company becomes a strategic enabler. By combining development and manufacturing under one roof, CDMOs help organizations translate complex chemistry into compliant, scalable, and commercially viable products, without operational risk.
Intermediates-focused custom chemical manufacturing CDMO, support customers from early development through commercial supply with precision and regulatory confidence.
What is a Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO)?
A Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization (CDMO) integrates the strengths of a CRO (Contract Research Organization) and a CMO (Contract Manufacturing Organization).
Unlike a CRO vs CMO manufacturer, a CDMO supports the entire product lifecycle, from R&D and process development to pilot-scale validation and commercial manufacturing.
What is a CDMO Company in Real Terms?
A CDMO company owns both the knowledge and the infrastructure needed to commercialize chemistry.
Example: Specialty Chemical Intermediate
A global specialty chemicals firm develops a novel intermediate for a performance coating. While lab synthesis is successful, the company lacks:
- Pilot reactors to validate scale behavior
- Expertise in impurity control at higher temperatures
- Manufacturing capacity aligned with EHS regulations
A CDMO partner:
- Optimizes the reaction pathway
- Conducts DOE studies to improve yield
- Validates safety and kinetics at pilot scale
- Transfers the process into commercial production
This integrated approach is the core value of CDMO partnerships.
This single-roof availability reduces handoff risks, shortens timelines, and improves manufacturability, key reasons why CDMO partnerships have become the preferred model for regulated and specialty markets.
Key Components of CDMO Services
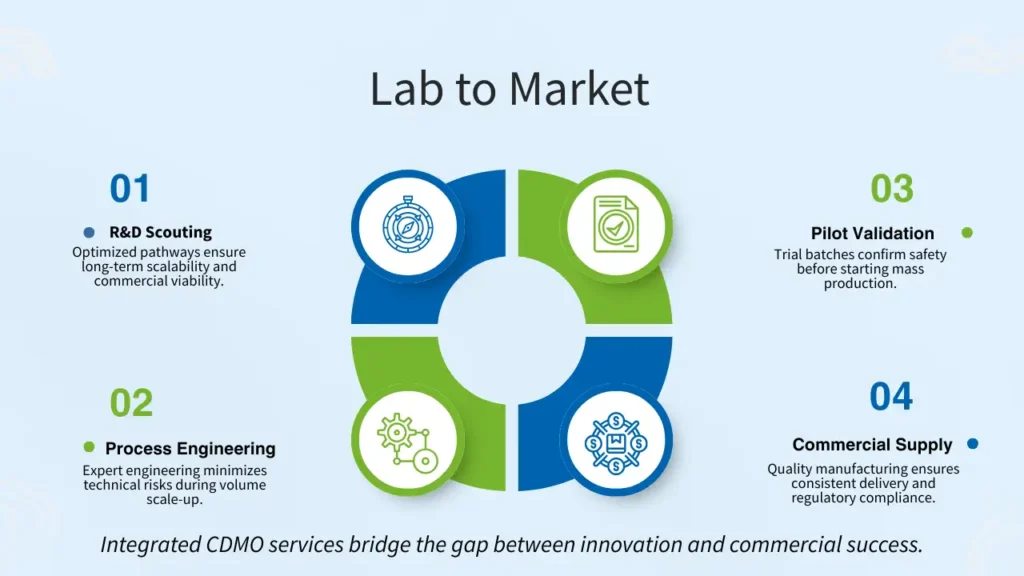
A high-performing CDMO delivers integrated CDMO solutions across development and manufacturing. The most critical components include:
1. R&D and CDMO Development
What it involves
- Route scouting and reaction pathway selection
- Raw material qualification
- Impurity identification and control
- Early cost-of-goods analysis
Use Case: An agrochemical intermediate shows excellent efficacy but produces trace impurities that exceed regulatory thresholds. CDMO partner for agrochemical companies redesign the synthesis route to minimize impurity formation without sacrificing yield.
Why it matters
Decisions made during CDMO development determine long-term manufacturability, regulatory acceptance, and commercial viability.
2. Process Engineering, Scale-Up & Optimization
What it involves
- Design of scalable reaction conditions
- Heat and mass transfer analysis
- Solvent and catalyst optimization
- Yield improvement and waste reduction
Use Case: A reaction that runs smoothly at 2-liter scale becomes uncontrollable at 2,000 liters due to exothermic behavior. The CDMO modifies agitation, cooling profiles, and addition rates to ensure safe, repeatable production.
Business Impact
- Reduced batch failures
- Lower production costs
- Improved plant safety
3. Pilot-Scale Validation
What it involves
- Pilot reactor runs
- Equipment compatibility testing
- Filtration and isolation trials
- Hazard and operability studies
Use Case: During pilot production, a CDMO identifies that filtration time exceeds acceptable limits. By changing filtration media and drying parameters, the process becomes commercially feasible.
Why pilot scale is critical: Skipping pilot validation often leads to costly rework at commercial scale.
4. Technology Transfer & Manufacturing Integration
What it involves
- Documentation standardization
- Knowledge retention across teams
- Seamless transition from development to plant
Use Case: Instead of transferring a process from an R&D lab to a third-party manufacturer, a CDMO executes both. This eliminates data loss, misinterpretation, and revalidation delays.
Key Advantage: Single-team ownership ensures continuity and consistency.
5. Commercial CDMO Manufacturing
What it involves
- Batch or continuous production
- Quality assurance and release testing
- Regulatory documentation and audits
- Supply-chain reliability
Use Case: A global customer requires uninterrupted supply of a regulated intermediate. The CDMO ensures batch consistency, audit readiness, and contingency planning—without the customer owning manufacturing assets.
Benefits of CDMO Services
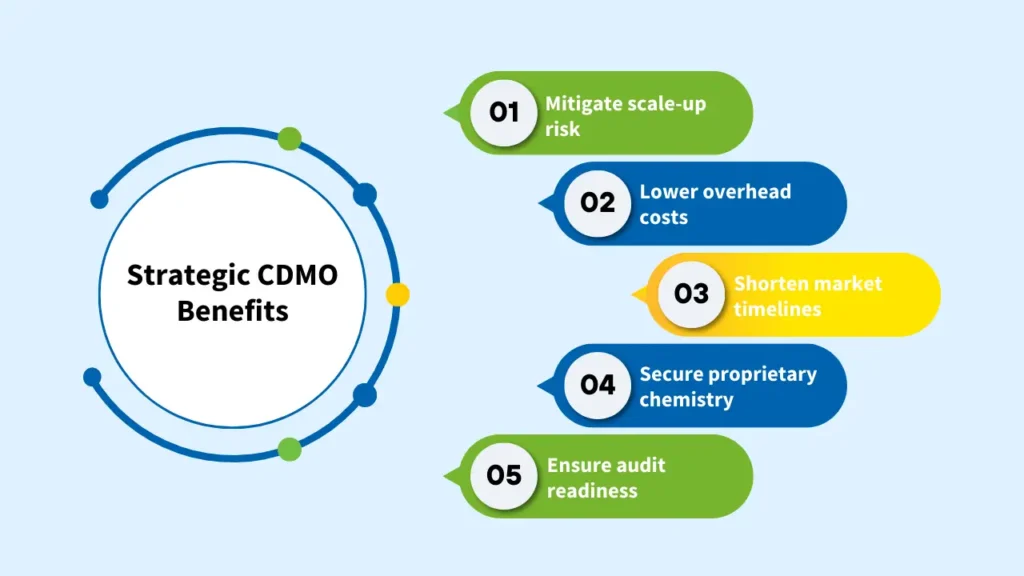
Partnering with a capable CDMO company delivers value far beyond outsourcing production. When executed correctly, CDMO partnerships become a strategic advantage that impacts cost structure, speed, compliance, and long-term scalability.
Below are the core benefits of CDMO services, explained.
1. Reduced Technical and Scale-Up Risk
One of the most significant advantages of working with a CDMO is early identification and mitigation of scale-up risks—the most common failure point in chemical commercialization.
For example: A specialty chemical intermediate shows a yield at laboratory scale. During pilot trials, the CDMO identifies heat buildup that could lead to thermal runaway at commercial volumes. By modifying reaction sequencing, cooling profiles, and agitation speed, the process becomes safe and reproducible at scale.
2. Faster Time to Market Through Parallel Execution
A well-structured CDMO accelerates commercialization by running development, validation, and manufacturing readiness in parallel, rather than sequentially.
For example: While a formulation is still being optimized, the CDMO begins pilot planning, raw material science, and equipment mapping. When development is finalized, pilot and commercial production can start immediately, cutting months from the launch timeline.
3. Capital Efficiency and Reduced Financial Exposure
Building and operating chemical manufacturing infrastructure requires high upfront capital investment and long payback periods. CDMO partnerships convert fixed costs into variable costs.
For Example: Instead of investing millions in a new reactor train for a single intermediate, a company leverages a CDMO’s existing infrastructure. Production scales based on demand, without locking capital into underutilized assets.
4. Built-In Regulatory and Quality Confidence
Operating in regulated markets demands robust quality systems, traceability, and audit readiness, capabilities that mature CDMO companies already possess.
For Example: A global customer requires extensive documentation for an intermediate used in regulated applications. The CDMO provides batch traceability, validated analytical methods, and audit-ready records, ensuring uninterrupted supply approval.
5. Improved Process Economics and Yield Optimization
Experienced CDMOs continuously optimize processes to make them commercially efficient.
Real-World Example: Through DOE studies, a CDMO improves reaction yield and reduces solvent consumption. Over annual production volumes, this translates into substantial cost savings.
6. Scalability Without Operational Disruption
Demand fluctuations are common in specialty and custom chemical markets. CDMOs provide the flexibility to scale production up or down without disrupting operations.
For Example: A product gains unexpected traction in a new application. The CDMO reallocates capacity and adjusts production schedules to meet increased demand, without the customer modifying its internal operations.
7. Strategic Focus for Internal Teams
Outsourcing to a CDMO allows internal teams to focus on innovation, market strategy, and customer engagement, rather than operational execution.
For Example: With manufacturing and scale-up handled by a CDMO, internal team can focus on next-generation formulations and application expansion.
8. Cost Competitiveness Beyond Simple Cost Savings
Cost competitiveness is not just about lower pricing—it is about optimized economics across the entire lifecycle.
How CDMOs create cost advantage
- Optimized batch sizing and reactor utilization
- Yield improvement through DOE studies
- Solvent recovery and waste minimization
- Shared infrastructure and procurement efficiencies
9. Intellectual Property (IP) Protection and Confidentiality
A common concern when outsourcing chemistry is IP security. Reputable CDMO companies operate under strict confidentiality, IP ownership clarity, and controlled access frameworks.
How CDMOs protect IP
- Clear IP ownership agreements
- Segregated project teams
- Controlled documentation access
- Secure data and sample handling
Real-World Example: A customer develops a proprietary synthesis route for a high-value intermediate. The CDMO executes manufacturing under strict confidentiality, ensuring the customer retains full IP ownership.
Considerations When Choosing a CDMO Partner
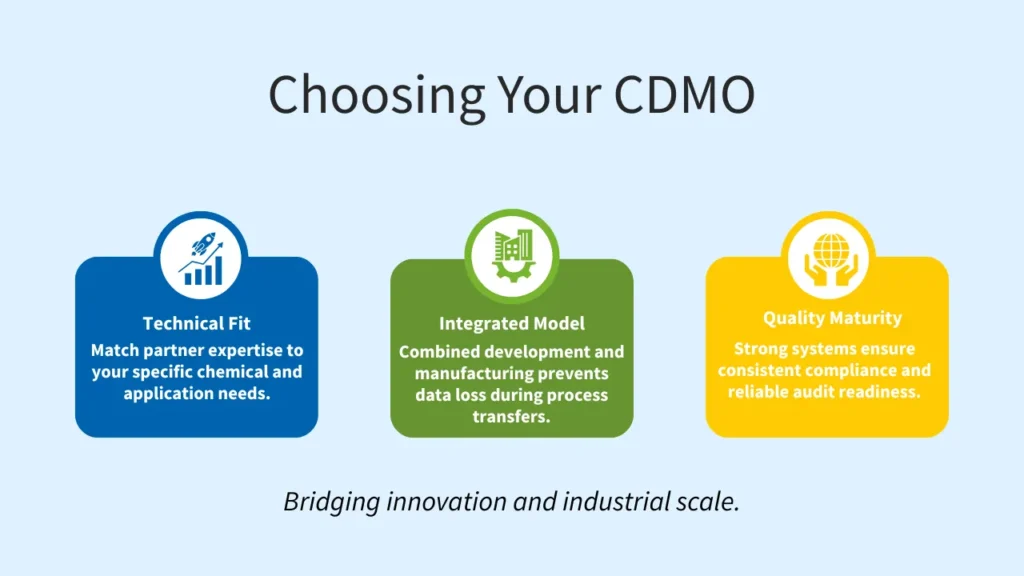
Selecting a CDMO partner directly influences product success, compliance outcomes, cost efficiency, and long-term supply resilience. The following criteria help enterprises evaluate CDMO companies objectively, beyond surface-level capabilities.
1. Chemistry and Application Alignment
A CDMO must demonstrate alignment with the specific chemistry class and end-use application, not just generic manufacturing competence. Application-driven requirements such as impurity thresholds, stability, and performance behavior must be understood at the process level.
| Evaluation Focus | What to Look For |
| Chemistry alignment | Prior work with comparable intermediates |
| Application awareness | Understanding of downstream performance needs |
| Process depth | Ability to manage complex, multi-step synthesis |
| Technical ownership | Strong in-house development capability |
2. Integrated Development and Manufacturing Model
CDMOs that operate development and manufacturing as a single, integrated system provide stronger execution consistency. Fragmented delivery models often introduce delays, misinterpretation, and process drift during commercialization.
| Evaluation Focus | What to Look For |
| Lifecycle coverage | Development through commercial production |
| Operational continuity | One accountable organization |
| Pilot readiness | In-house pilot-scale validation |
| Knowledge flow | Seamless transition across stages |
3. Quality, Safety, and Regulatory Maturity
Robust quality systems and EHS governance are foundational for reliable CDMO manufacturing. Mature CDMO companies embed compliance into daily operations rather than treating it as a reactive requirement.
| Evaluation Focus | What to Look For |
| Quality systems | Structured, audit-ready frameworks |
| Traceability | End-to-end batch documentation |
| Safety culture | Proactive EHS management |
| Regulatory exposure | Experience with global customers |
4. Commercial Scale Execution Capability
The ability to consistently deliver at commercial scale separates development-focused vendors from true CDMO partners. This includes engineering rigor, operational discipline, and repeatability under real-world conditions.
| Evaluation Focus | What to Look For |
| Scale execution | Proven commercial production |
| Engineering strength | Robust process and plant engineering |
| Volume flexibility | Adaptability across batch sizes |
| Operational stability | Consistent output and quality |
5. Affordability and Sustainable Cost Structure
Affordability in a CDMO context is driven by process efficiency, yield control, and resource optimization, not by short-term pricing concessions. Sustainable economics matter more than initial quotations.
| Evaluation Focus | What to Look For |
| Process efficiency | Optimized yields and cycle times |
| Resource utilization | Solvent recovery and waste minimization |
| Cost transparency | Predictable, explainable pricing |
| Scale economics | Stable cost behavior at higher volumes |
6. Long-Term Collaboration Orientation
CDMO engagements deliver maximum value when structured as long-term collaborations rather than transactional manufacturing arrangements. A partnership-driven model supports continuous improvement and supply reliability.
| Evaluation Focus | What to Look For |
| Engagement model | Long-term relationship focus |
| Improvement mindset | Ongoing optimization initiatives |
| Communication discipline | Structured governance and reviews |
| Accountability | Clear ownership and responsiveness |
At Novopor, we are CDMO experts in custom chemical manufacturing and intermediates, delivering:
- Complex multi-step chemistry expertise
- Integrated CDMO development and manufacturing
- Pilot-to-commercial scalability
- Strong quality, EHS, and regulatory governance
Conclusion
Understanding what is a CDMO company is essential for organizations navigating complex chemistry, regulatory scrutiny, and commercial scale-up.
A capable contract development manufacturing organization does more than manufacture—it reduces risk, improves manufacturability, and ensures consistent product performance from lab to market.
By carefully selecting a CDMO partner with proven integration, scale-up expertise, and compliance rigor, enterprises can accelerate innovation while protecting quality and supply continuity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Risks include poor tech transfer or limited scale-up expertise, mitigated by selecting experienced CDMO companies with integrated teams.
Evaluate chemistry expertise, scale-up history, quality systems, EHS compliance, and partnership mindset.
The US hosts multiple CDMO companies supporting custom and specialty chemical manufacturing; selection depends on chemistry and compliance needs.
A CDMO integrates development, pilot validation, and manufacturing to ensure seamless scalability and compliance.
A CMO focuses only on manufacturing, while a CDMO supports both development and manufacturing across the full lifecycle.




